16 Rules of Effective UX Writing

UX writing is the practice of crafting UI copy that guides users within a product and helps them interact with it. UI copy includes buttons and menu labels, error messages, security notes, terms and conditions, as well as any instructions on product usage.
The primary aim of UX writing is to settle communication between users and a digital product. In this article, I'll provide some practical tips on effective UX writing.
Why crafting UI text should be an integral part of design process
All too often product developers think of UI text as something that belongs to product documentation phase."First we'll design the product, and then we'll hire someone to help us write a UI copy." Such assumptions often cause a lot of harm because critical UI issue can go unnoticed until the later stages of product development process. That's why UI text should be written earlier in the process.
Work on text early because text problems often reveal design problems.
Professional UX writers should work together with software developers and designers on crafting UI text. As a part of this activity, they often ask product team to explain design decisions. If a team has trouble explaining a design, quite often it is the design, not the text copy, that needs improving.
Tips On Writing UI Text
Writing the copy that are part of the UI design is both an art and science. While it's impossible to provide universal rules for writing UI text, it's possible to provide some general rules that can help you create better UX.
1. Be concise
Concise doesn't mean limited; it means something closer to efficient. Use as few words as possible without losing the meaning. When writing concisely, we make sure every word on the screen has a job. Follow Mark Twain's advice:
"Writing is easy. All you have to do is cross out the wrong words."
Don't: You must log in before you can write a comment
Do: Log in to comment
2. Avoid long blocks of text
When using a product, users aren't immersed in the user interface itself but in their work. Consequently, users don't read UI text - they scan it. Help them scan the text by writing it in short, scannable blocks. Chunk text into shorter sentences and paragraphs. Keep the most important text up front and then ruthlessly edit what comes after it.
Write short and then cut it into half
3. Avoid double negatives
Double negatives increase cognitive load - they make users spend extra time decoding the message.
Don't: I do not want to unsubscribe
4. Begin with the objective
When a sentence describes an objective and the action needed to achieve it, start the sentence with the objective.
Don't: To see item's properties, tap on it
Do: Tap on item to see it's properties
5. Use specific verbs whenever possible
Specific verbs (such as connect or save) are more meaningful to users than generic ones (such as configure or manage).
6. Make the copy consistent
Inconsistency creates confusion. One typical example of inconsistency is replacing a word with a synonym in a different part of the UI. For instance, if you decide to call the process of arranging something "Scheduling" in one part of UI do not call it a "Booking" in other parts of your UI.
Another common pitfall is combining forms of address. Don't refer to the user in both the second person and the first person within the same phrase.
Don't: Change your preferences in My Account
Do: Change your preferences in Your Account
7. Avoid jargon
One of the significant characteristics of effective UX writing is clarity and simplicity. For clarity, you need to remove the technical terms and use familiar, understandable words and phrases instead. It's especially important to avoid jargon in error messages.
Don't: System error (code #2234): An authentication error has occurred
Do: Sign-in error: You entered an incorrect password
8. Write in present tense
Avoid using the future tense to describe the action.
Don't: Video has been downloaded
Do: Video downloaded
9. Write in the active voice
The passive voice makes readers yawn. Compare this sentence in both voices:
Don't: The Search button should be clicked when you are ready to search for an item.
Do: Click the Search button to search for an article.
10. Use numerals
Use numerals in place of words for numbers.
Don't: You have 2 missed calls
Do: You have two missed calls
11. Avoid showing all details up front
Sometimes it might be helpful to provide additional information or supplemental instruction for users. But all too often such details are presented upfront. Too much information can quickly overwhelm users. Thus, reveal detail as needed. Use a mechanism of progressive disclosure to show more details. In the most basic form, this mechanism can be implemented as 'Read more' link to the full content.
When labeling buttons and other interactive elements, use action verbs, such as 'Connect,' 'Send,' 'Subscribe' instead of vague 'Okay' or 'Submit.'
13. Be careful when using humor
A lot of designers say that incorporating humor in UI makes it sound more human. But similar to any other component of UI, humor should be designed. People are likely to read the text in your interface many times, and what might seem clever at first can become irritating over time (especially if you use humor in error messages). Also, remember that humor in one culture doesn't necessarily translate well to other cultures.
14. Use language that's consistent with the user's platform
The terms we use when describing interaction with a desktop app do not necessarily apply to mobile platforms. For example, if you design an iPhone app, we can't say 'click' when referring to the action. We need to say 'tap' instead.
15. Use 'today,' 'yesterday' or 'tomorrow' instead of a date
People don't use the date when they refer to the day before the present day. They say 'yesterday.' The same principle can be applied to UIs. Instead of giving a date, say 'today,' 'yesterday' or 'tomorrow.' It prevents users from using calendar each time they want to know when the event happened. But remember that these terms can be confusing or inaccurate if you don't account for the current locale.
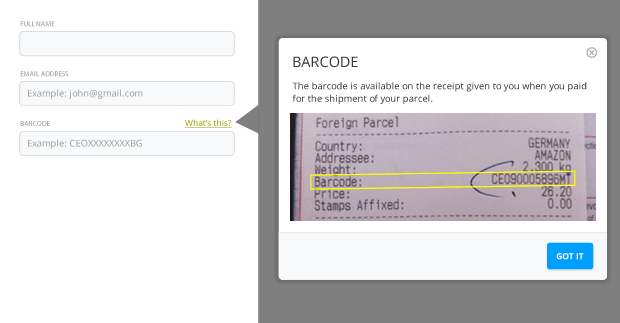
16. Use graphics if they will help you communicate
Human beings are incredibly visual creatures. An ability to interpreting visual information is hard-wired into our brains. In some context, it might be nearly impossible to say something in words. That's where imagery can support us and make text comprehensible. Below is an example which helps users to find specific information.